How Can a Diabetic Wound Heal Faster: 10 Strategies to Pick

Table of content
Diabetes can have challenges when it comes to wound curing due to cooperated circulation and decreased immune response. Even minor wounds or cuts cause a serious concern. High blood sugar, poor circulation, and nerve damage slow healing, increasing the risk of infections and complications. Handling diabetic injuries needs cautious care and active actions to confirm they heal correctly and reduce the danger of complications like infections. Here are some important strategies to aid in the quicker healing of diabetic wounds:
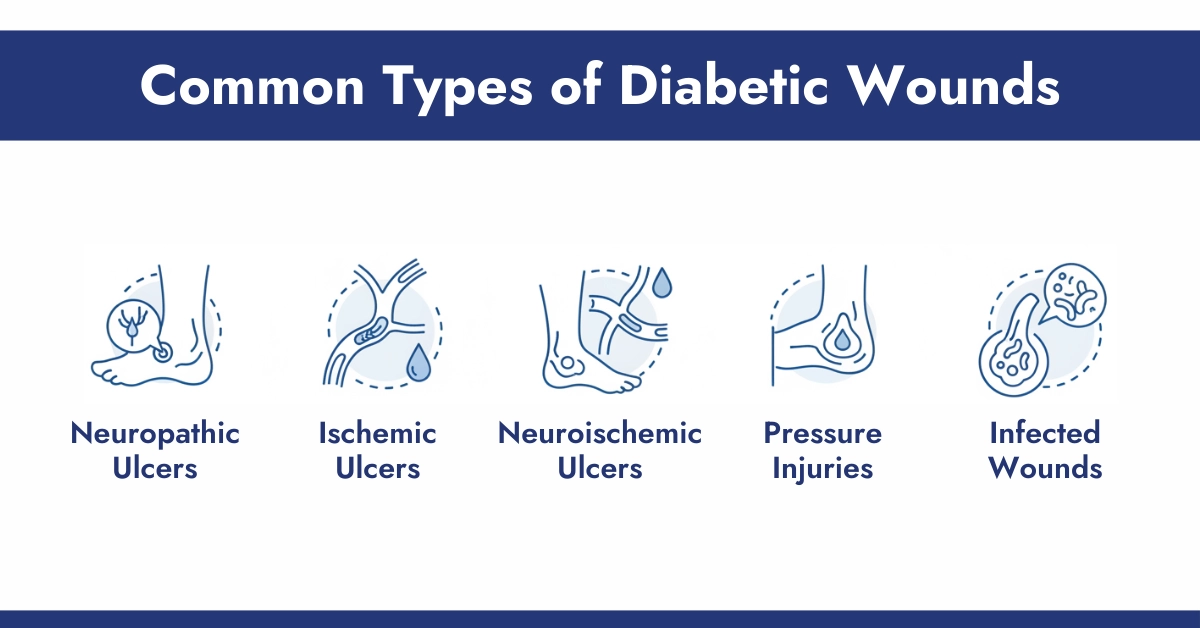
Common Types of Diabetic Wounds
Diabetic wounds appear in various forms, each with distinct features and causes. Here are the main types and what sets them apart.
1. Neuropathic Ulcers
- Cause: Nerve damage (neuropathy) leading to loss of sensation in the feet.
- Appearance: Usually on the soles, under pressure points like the ball of the foot or big toe joint; often deep and painless.
- Risk: Injuries go unnoticed, increasing chances of infection.
2. Ischemic Ulcers
- Cause: Poor blood flow from peripheral artery disease.
- Appearance: Toes or heels may show small, deep sores with cool, bluish skin.
- Risk: Reduced blood flow slows healing and raises infection/gangrene risk.
3. Neuroischemic Ulcers
- Cause: Combination of neuropathy and poor circulation.
- Appearance: Features of both neuropathic and ischemic ulcers.
- Risk: Difficult to heal, higher chances of severe complications.
4. Pressure Injuries
- Cause: Prolonged pressure on bony areas, common in immobile individuals.
- Appearance: Red or discolored areas over heels, hips, or elbows, which may develop into open sores.
- Risk: Can cause deep tissue damage and infections.
5. Infected Wounds
- Cause: Bacterial invasion.
- Appearance: Redness, swelling, warmth, pus, or foul odor.
- Risk: Rapid spread can lead to cellulitis, osteomyelitis, or sepsis.
Common Causes of Diabetic Wounds
- Neuropathy: Nerve damage reduces sensation, making small injuries go unnoticed.
- Peripheral Artery Disease: Poor circulation slows healing and limits oxygen/nutrient supply.
- Weakened Immune System: High blood sugar impairs infection-fighting ability.
- Foot Deformities: Conditions like bunions or hammertoes increase pressure points.
- Other Factors: Poorly fitting shoes, smoking, uncontrolled blood sugar, or repeated trauma.

Diabetic Wound Care Strategies to Heal Wounds
1. Understanding Healing Time for Diabetic Wounds
Diabetic wounds naturally take longer to heal due to reduced blood flow, neuropathy, and immune system impairment. While a minor cut may take a few days in healthy individuals, a diabetic wound can linger for weeks or even a year if not properly managed. Early attention, proper wound care, and glucose management with the use of cgm sensors, including Libre 3 Plus or Dexcom G7 (Only for adult) are crucial to accelerate healing safely.
2. Preventing Infection in Diabetic Wounds
Common bacterial and viral infections are the most dangerous complication of diabetic wounds. Even small wounds can become life-threatening if bacteria or a virus enter the body.
Tips to prevent infection:
- Clean the wound immediately with mild soap and water.
- Apply an antibacterial ointment or antiviral drugs recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Use sterile dressings and change them daily or when they get wet or dirty.
- Watch for warning signs: redness, swelling, pus, warmth, or foul odor.
When to see a doctor: If you notice spreading redness, fever, or pain that intensifies, seek medical care immediately.
3. Controlling Blood Sugar for Faster Healing
High or fluctuating blood sugar levels slow down wound healing by impairing white blood cell function and reducing collagen formation. Consistently managing glucose can significantly improve recovery time.
Practical tips:
- Monitor blood sugar levels with Cgm sensors multiple times a day.
- Follow a diabetic-friendly meal plan.
- Take medications or insulin as prescribed by a healthcare specialist.
- Avoid sudden spikes from sugary foods or drinks.
4. Effective Wound Care Techniques
Proper wound care is critical for healing. This includes cleaning, dressing, and protecting the wound from further injury.
Best practices:
- Wash your hands thoroughly or use gloves before touching the wound.
- Gently clean with mild soap or saline solution.
- Cover with sterile, breathable dressings.
- Change dressings as directed, keeping the wound dry and protected.
5. Medical Treatments & Professional Interventions
While home care is essential, medical interventions may be necessary for more serious wounds.
Advanced treatments:
- Debridement: Removal of dead tissue to encourage new growth.
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: Increases oxygen supply to tissues.
- Growth factor treatments: Stimulate tissue regeneration.
Alert: CGM Monitors is the trusted supplier of CGM devices. We do not recommend any prescription or guidance on medical drug. Feel free to ask your healthcare physician before taking any steps because the CGM Monitors’ team always love their customers.
6. Diet and Nutrition to Support Healing
Nutrition plays a major role in tissue repair and recovery. Certain vitamins and minerals help the body heal faster.
Nutrients You May Use After consulting with doctors:
- Protein: Supports collagen formation and tissue repair.
- Vitamin C: Boosts immunity and tissue growth.
- Zinc: Helps with cell regeneration.
- Vitamin A: Promotes skin integrity and healing.
Incorporate foods like diabetic friendly dry fruits, lean meats, fish, eggs, leafy greens, citrus fruits, nuts, and seeds. Consider supplementation if dietary intake is insufficient.
7. Lifestyle Factors That Influence Healing
Healthy habits can significantly speed up wound recovery.
Important considerations:
- Diabetic Friendly Exercise: Enhances circulation, delivering nutrients to wounds. Avoid activities that put pressure on the wound. Here is the link for the best diabetic-friendly home exercise.
- Core Sleep: Proper sleep allows the body to repair tissue.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol: Both impede healing and increase infection risk.
8. Foot and Skin Care for Diabetics
Preventing wounds is just as important as healing them. Diabetic neuropathy can make it hard to detect injuries.
Preventive measures:
- Inspect feet daily for cuts, blisters, or redness.
- Keep skin moisturized to prevent cracks.
- Wear comfortable, protective footwear.
- Regularly visit a podiatrist for check-ups.
9. Complications and Risks of Slow-Healing Wounds
Slow-healing wounds can lead to severe complications if neglected. Risks include:
- Infections leading to cellulitis or sepsis
- Chronic ulcers requiring surgical intervention
- In extreme cases, amputation
Warning signs to watch for: Persistent redness, foul odor, increasing pain, or swelling. Early medical attention is critical.
10. Safe Home Remedies vs Medical Advice
While some home remedies can support healing, others may be harmful.
- Safe home practices:
- Gentle cleansing with saline or mild soap
- Using sterile dressings
- Applying doctor-approved ointments
Dangerous practices: Avoid applying harsh chemicals, herbal pastes, or untested remedies. Always consult your healthcare provider before trying new treatments.
Conclusion
Healing diabetic wounds faster requires a multi-faceted approach—from controlling blood sugar and practicing proper wound care to maintaining a nutritious diet and healthy lifestyle. Early intervention, infection prevention, and professional guidance are essential to prevent serious complications. By following these 10 strategies, diabetics can improve wound healing outcomes and maintain overall health.
Remember: Never ignore a wound that isn’t healing. Proper early action saves limbs and lives.
References:
Frequently Asked Question
How can a diabetic wound heal faster with home remedies?
For diabetic patients, supporting faster wound healing at home starts with tight blood sugar control through diet and monitoring with the use of a Dexcom sensor or Libre, as this improves circulation and immune function. Focus on a protein-rich, nutrient-balanced diet and daily foot checks, but always combine these steps with professional medical guidance rather than relying on them alone.
How do I properly clean a diabetic wound at home?
Diabetic patients should wash their hands first or use gloves, then gently rinse the wound with lukewarm saline solution or clean water to remove any debris without using harsh soaps, hydrogen peroxide, or alcohol that could damage tissue. Pat the area dry with a clean towel and apply a sterile dressing as recommended.
How does blood sugar control impact diabetic wound healing speed?
For people with diabetes, keeping blood sugar in a stable target range directly speeds up wound healing by supporting better blood flow, oxygen delivery, and immune cell activity at the injury site. High glucose levels thicken blood, prolong inflammation, and slow tissue repair, often leading to complications.
How can infection be prevented in a diabetic wound to accelerate healing?
Diabetic patients can help prevent infection and promote faster healing by keeping the wound clean, covered with sterile dressings, and free from pressure through proper offloading or elevation. Daily foot inspections for redness, swelling, or warmth, combined with strict blood sugar management, strengthen the body’s defenses against bacteria.[/vc_toggle
What are the common complications that delay diabetic wound healing?
In diabetic patients, common complications include reduced blood circulation that limits oxygen and nutrients, nerve damage (neuropathy) that allows wounds to worsen unnoticed, and weakened immunity from high blood sugar that invites infections. These issues often cause ongoing inflammation and tissue breakdown.
What are the most effective treatments for speeding up diabetic wound healing?
The most effective treatments for diabetic patients typically involve professional wound cleaning to remove dead tissue, specialized moist dressings, and devices that relieve pressure on the affected area. Pairing these with excellent blood sugar control and, when necessary, prescribed medications or therapies provides the best results.
What natural remedies are safe for diabetic wound care?
Diabetic patients should only consider natural approaches like medical-grade honey for its mild antibacterial properties under direct medical supervision, as many untested substances can irritate skin or delay healing. Focus instead on safe basics such as staying hydrated, eating nutrient-rich foods, and maintaining cleanliness.
What advanced therapies are available for diabetic wound healing?
Advanced therapies for stubborn diabetic wounds include negative pressure wound therapy to promote new tissue growth by removing fluid, bioengineered skin substitutes that support regeneration, and hyperbaric oxygen treatment to boost oxygen supply.
Why is it important to keep a diabetic wound covered during healing?
For diabetic patients, covering a wound protects it from dirt, bacteria, and further injury while maintaining a moist environment that encourages healthy cell growth and prevents slow-drying scabs. This barrier supports faster tissue repair and reduces infection risk in skin that heals more slowly. Change dressings regularly as instructed to keep the area clean and protected.
Why do diabetic wounds heal slowly compared to non-diabetic wounds?
Diabetic wounds heal more slowly because high blood sugar damages blood vessels, reducing oxygen and nutrient delivery, while neuropathy often prevents early detection of injury. The immune response is also weaker, leading to prolonged inflammation and higher infection chances.











Write a comment
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required