Table of content
- Most Common Places to Inject Insulin
- Best Injection Sites for Slim or Obese Individuals
- How Often Should You Change Insulin Injection Sites?
- Precautions to Follow When Injecting Insulin
- Impact of Injecting Insulin at Different Locations
- Do’s and Don’ts of Injection Site Location for Insulin
- Frequently Asked Questions
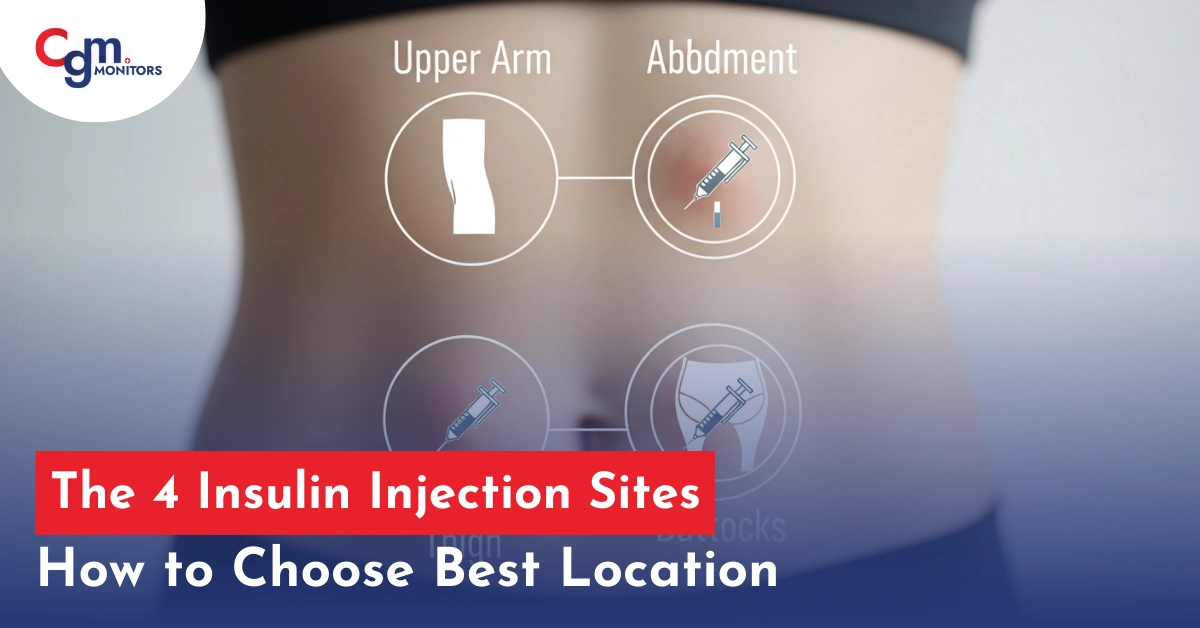
Most Common Places to Inject Insulin
While the abdomen, thighs, buttocks, and the back of the upper arm are all insulin injection sites, the best location for insulin injection may depend on certain factors, e.g., selecting the buttocks while self-injecting insulin may not be a feasible idea; moreover, if someone is aiming for rapid absorption, abdomen may be a suitable selection.
Insulin injections are an essential part of daily life for many people with diabetes, and selecting the proper injection sites for insulin ensures better absorption and fewer side effects. Here we have discussed all 4 insulin injection sites, their benefits, and important considerations when choosing where to inject insulin.
1. Abdomen: The Most Common Injection Site
The abdomen is widely considered the best place to inject insulin, offering a large surface area for effective absorption. Here’s why:
- Quick absorption: Insulin is absorbed quickly in the abdomen, especially when injected at least 2 inches away from the belly button.
- Easier to access: You can reach the area easily, and there are fewer muscles and nerves.
- How to inject: Pinch up a fold of skin, inject at a 90-degree angle, and rotate between the right and left side of the abdomen.
Do’s & Don’ts:
- Do inject at least 2 inches away from the belly button.
- Don’t inject in areas with scars or hardened skin.
Still Using Fingersticks?
Continuous glucose monitors like the Freestyle Libre 3 Plus Sensors help you track glucose in real-time and can work with AID systems such as Omnipod 5 and MiniMed 780G for automated insulin delivery
2. Thighs: A Comfortable Choice for Many
The thigh is another preferred injection site for insulin. The upper outer thigh offers a good option for sub Q insulin injection sites, and it tends to have a slower absorption rate compared to the abdomen. This might be beneficial for some, depending on their insulin regimen.
- Absorption speed: Slower than the abdomen, but still effective.
- Best technique: Pinch the skin and inject at a 90-degree angle, ideally in the upper outer thigh area.
Do’s & Don’ts:
- Do alternate between the left and right thighs to avoid tissue buildup.
- Don’t inject too close to the knee or hip joint.
3. Buttocks: A Less Common, But Viable Option
The buttocks provide a large area for insulin injection, though it may not be as commonly used due to accessibility.
- Absorption speed: Similar to the thigh, but can be slower.
- How to inject: Choose the upper outer quadrant of the buttock and inject at a 90-degree angle after pinching the skin.
Do’s & Don’ts:
- Do use the upper part of the buttock for better absorption.
- Don’t inject into the middle part of the buttock, where large nerves are located.
4. Arms: A Convenient and Effective Site for Some
The arms are less popular but still effective for insulin shots. The outer part of the upper arm is a good sub-Q insulin injection site, especially for individuals who are slim or those who prefer more discreet injections.
- Absorption speed: Slightly slower than the abdomen but still efficient.
- Injection technique: Pinch the skin on the upper arm and inject at a 90-degree angle.
Do’s & Don’ts:
- Do inject in the outer area of the upper arm.
- Don’t inject into muscle tissue or near the inner arm.
Attention:
Type 2 people who regularly inject insulin, or type 1 insulin-dependent individuals, may both opt for AID systems and get rid of multiple insulin injections. Get a free eligibility check with CGM Monitors now.

Best Injection Sites for Slim or Obese Individuals
For individuals with different body types, such as slim or obese individuals, the best location for insulin injection may vary.
- Slim individuals: It’s often easier to inject in the abdomen or arms as there’s less fatty tissue in other areas. When using the abdomen, make sure to pinch a fold of skin to avoid injecting into muscle.
- Obese individuals: For people with more fatty tissue, the thighs or abdomen may provide the most comfortable and effective spots. However, insulin injection sites should always be rotated to avoid lipodystrophy (fat buildup at the injection site).
How Often Should You Change Insulin Injection Sites?
It is essential to rotate insulin sites to prevent skin issues like insulin injection site complications. The best place to inject insulin is not always the same, and regular site rotation helps avoid lipohypertrophy (lumps or hardening of fatty tissue).
- How often: Rotate between at least 4 different sites (abdomen, thighs, arms, buttocks). This will reduce the risk of complications and improve insulin absorption.
- Don’t use the same spot frequently. Overuse of an area can cause tissue damage.
Precautions to Follow When Injecting Insulin
1. Pinch-Up Skin Technique
To prevent injecting into the muscle, always use the pinch-up technique. This helps ensure that the insulin is administered into the fatty tissue (subcutaneous layer) and not into the muscle.
2. Avoid the Belly Button
When using the abdomen for insulin injections, inject at least 2 inches away from the belly button. This is crucial for accurate absorption, as the belly button area is prone to poor absorption due to scar tissue.
3. Gestational Diabetes
When self-injecting insulin during pregnancy (gestational diabetes), it’s essential to choose insulin injection sites that ensure comfort and safety. The abdomen is often preferred, but the harder part of the abdomen should not be selected. The pinch-up skin rule should be followed, and consulting your doctor for the best approach for your situation is always recommended.
4. Insulin Pen Usage
If you are using an insulin pen, follow these guidelines:
- Setting the number: Dial the correct insulin dose based on your prescription.
- Best places to inject: The abdomen or thighs are generally preferred for insulin pens, as these sites have a larger surface area for insulin absorption.

Impact of Injecting Insulin at Different Locations
Injecting insulin in various insulin sites can have different effects:
- Speed of absorption: The abdomen is absorbed quickly, while the thighs and buttocks tend to absorb more slowly.
- Consistency: Rotating injection sites ensures that insulin absorption remains consistent and helps prevent insulin injection site complications like lipohypertrophy.
Do’s and Don’ts of Injection Site Location for Insulin
| Do’s | Don’ts |
| Rotate between different areas. | Inject into muscle or veins. |
| Inject at least 2 inches away from the belly button. | Inject into scar tissue or hard lumps. |
| Pinch the skin to avoid muscle tissue. | Reuse a single site repeatedly. |
| Use insulin pens properly for accurate doses. | Inject too deep or shallow. |
By following these tips and guidelines, you can ensure the best location for insulin injection, reducing discomfort and improving your insulin management.
If you have any doubts or concerns, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider or refer to resources like CGM Monitors for further guidance on insulin injections.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to self inject insulin?
In case of using an injection and a vial:
Clean your hands and clean the injecting area with an alcohol wipe.
Pull up the plunger till the point of the required insulin dose, e.g., 10 units.
Remove the cap of your syringe.
Put the needle inside the vial, move it upside down, and fill the required amount of insulin.
Pinch about 2 inches of skin. In a single smooth go, put the syringe in.
Push down the plunger and wait for about 5 seconds, then pull back the injection.
Where to inject insulin?
Insulin sites include the abdomen (2 inches away from the belly button), thighs, buttocks (upper outer quadrant), and the back of the upper arms.
What is the primary function of insulin?
Insulin helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream, which the body then uses for energy or stores for future use.
Should you change location for insulin injections?
Yes, insulin sites should be changed and rotated. Repeated injections in the same spot may lead to lipohypertrophy.






Write a comment
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required