Table of content
Dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, is a common issue for many people with diabetes. If you’ve been experiencing an unusual level of dryness in your mouth, it’s important to understand how diabetes might be contributing to this problem and what you can do to manage it. In this blog, we’ll explore the connection between diabetes and dry mouth, its causes, and practical solutions to help you find relief.
What is Dry Mouth: Xerostomia?
Xerostomia is the sensation of having insufficient saliva in the mouth. In diabetes, it can manifest as:
- A dry or “cottony” feeling in the mouth.
- Chapped or dry lips.
- A sticky sensation on the lips.
- Dryness or irritation in the throat.
Unlike occasional mouth dryness from dehydration or environmental factors, diabetes-related dry mouth is chronic and persistent, often interfering with eating, speaking, and swallowing. People with diabetes dry lips may notice discomfort, especially in the morning or at night, signalling the need for better blood sugar and oral management.
Diabetes and Dry Mouth Connection
Does diabetes cause dry mouth? Yes, people with diabetes often experience dry mouth (xerostomia) due to hyperglycemia, which can reduce saliva production and cause dryness or discomfort, such as a cottony feeling in the mouth, dry or sticky lips, and a dry throat. If you wake up early in the morning, you feel your mouth is dry even after drinking water, you still feel thirsty or dryness in your mouth.
Poorly controlled diabetes can also increase the risk of oral infections and tooth decay because saliva helps wash away bacteria and maintain oral health. Staying hydrated, managing blood sugar levels with Libre or Dexcom CGMs and insulin pumps, and practising good oral hygiene can help reduce the impact of dry mouth for diabetic patients.
Common Dry Mouth Causes in Diabetes
Several factors contribute to dry mouth in diabetes, ranging from blood sugar imbalances to medication side effects.
a. High Blood Sugar Levels
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, causes your body to lose fluids, leading to dehydration. This directly affects saliva production, causing dry mouth blood sugar issues. People with uncontrolled diabetes may often feel thirsty and notice persistent mouth dryness.
b. Low Blood Sugar Episodes
Interestingly, low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can also trigger dry mouth. During hypoglycemia, the body responds with stress hormones that reduce saliva flow. People may wonder, can low blood sugar cause dry mouth? Yes, especially if blood sugar swings are frequent.
c. Diabetes Medications
Certain medications used to manage diabetes can cause xerostomia. For instance:
- Metformin dry mouth: Commonly reported by users, sometimes worse at night
- Insulin: Rarely, insulin therapy may contribute indirectly to dry mouth
- Other diabetes medications may reduce saliva production or alter oral pH
d. Nerve and Salivary Gland Damage
Long-term diabetes can lead to neuropathy, affecting the nerves that control salivary glands. Damage to these nerves results in chronic diabetes xerostomia, where the mouth feels dry regardless of fluid intake.
After discussing the common causes of dry mouth, we come to the point that hyperglycemia is the reason, and this condition is caused by poor diabetes management. What do you do? CGM Monitors always care for patients with diabetes and recommend using 15-day CGM sensors like the Dexcom G7 to help you manage your glucose levels.

Common Dry Mouth Diabetes Symptoms
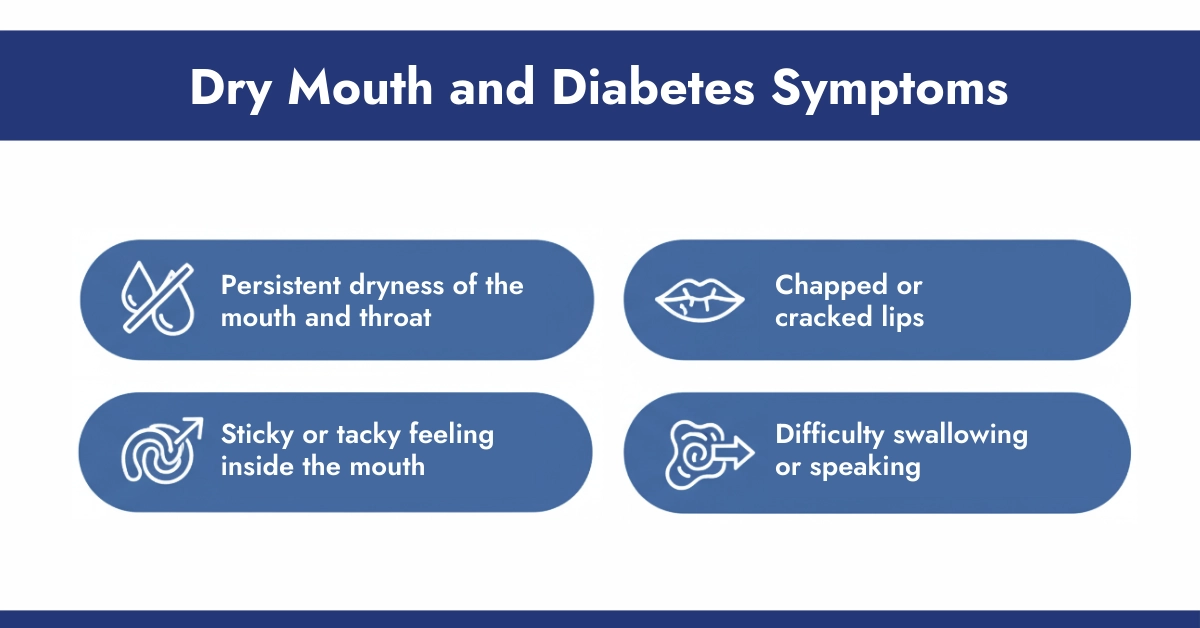
Dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, is a common symptom in people with diabetes. Recognizing it early can help manage discomfort and prevent complications. Key signs include:
1. Persistent dryness of the mouth and throat
People with diabetes may feel constant dryness in their mouth or throat, even after drinking water. This can make talking, eating, and swallowing uncomfortable.
2. Chapped or cracked lip
Reduced saliva can lead to dry, chapped, or cracked lips. This symptom may worsen in cold or dry weather and can cause soreness or bleeding if left untreated.
3. Sticky or tacky feeling inside the mouth
A sticky or tacky sensation on the tongue or roof of the mouth is often noticeable in diabetes-related dry mouth. It can make it difficult to taste food properly and affect oral hygiene.
4. Difficulty swallowing or speaking
Severe dryness can interfere with normal speech or swallowing. People may find it harder to chew or swallow certain foods and may notice their voice becoming hoarse.
Understanding these symptoms is important for distinguishing between occasional dryness and xerostomia caused by diabetes. Managing blood sugar levels, staying hydrated, and using saliva substitutes can help alleviate discomfort and protect oral health.
Health Risks of Untreated Dry Mouth
Neglecting dry mouth in diabetics can lead to serious oral health issues:
- Cavities and tooth decay: Saliva protects teeth; lack of it increases risk
- Gum disease (gingivitis or periodontitis)
- Oral infections: Fungal infections like thrush are common
- Impact on blood sugar control: Difficulty eating due to dry mouth can affect nutrition and glucose management
How to Stop Dry Mouth with Diabetes with Remedies and Treatments
a. Lifestyle & Home Remedies
Simple adjustments can reduce diabetes dry mouth symptoms:
- Stay hydrated: Drink water regularly
- Check blood sugar regularly: Use Dexcom G7 or Libre 3 Plus to monitor your sugar level every 5 minutes.
- Reduce sugar intake: Excess sugar worsens dehydration and oral bacteria growth.
- Avoid alcohol and caffeine: Both can dehydrate the body.
- Use sugar-free gum or lozenges: Stimulates saliva production.
- Maintain good oral hygiene with gentle brushing.
b. Medical Treatments
For persistent xerostomia diabetes, medical options include:
- Prescription saliva substitutes or oral moisturizers
- Adjusting diabetes medications under a doctor’s supervision to reduce side effects
- Regular dental check-ups to manage oral complications
When to Seek Professional Help
If diabetes and dry mouth persist despite trying these measures, or if it leads to severe discomfort or complications, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider or dentist. They can help determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatments or adjustments to your diabetes management plan.
Conclusion
The connection between diabetes and dry mouth is strong and often overlooked. Persistent xerostomia can lead to oral health problems, discomfort, and even affect blood sugar control. Proactive management through hydration, oral care, lifestyle changes, and regular medical consultations can significantly improve quality of life for people with diabetes. Understanding your symptoms and acting early is the key to preventing long-term complications.
References:
- Cleveland Clinic: Diabetes and Dry Mouth
- Healthline: Dry Mouth Diabetes
Frequently Asked Questions
How does diabetes cause dry mouth?
Diabetes often leads to dry mouth because high blood sugar levels can reduce saliva production in the salivary glands, leading to dehydration and impaired moisture in the mouth. This condition, known as xerostomia, is exacerbated by frequent urination that depletes body fluids, making the oral environment feel parched and uncomfortable for many patients.
How can diabetics alleviate dry mouth symptoms effectively?
Diabetics can alleviate dry mouth by staying well-hydrated with frequent sips of water, using sugar-free lozenges or gum to stimulate saliva flow, and avoiding caffeine or alcohol which can worsen dehydration. Maintaining good blood sugar control through diet and using CGM sensors listed on CGM Monitors also helps reduce the severity of symptoms over time.
What is the connection between diabetes and dry mouth?
The connection between diabetes and dry mouth stems from elevated glucose levels that disrupt saliva production and cause overall dehydration due to increased urination. This results in a drier oral cavity, increasing the risk of related issues like infections, and it’s a common indicator of uncontrolled blood sugar in diabetic individuals.
What are the early signs of dry mouth in diabetics?
Early signs of dry mouth in diabetics include a persistent sticky or dry feeling in the mouth, difficulty swallowing or speaking, and a burning sensation on the tongue. Patients may also notice cracked lips, increased thirst, or a change in taste, signaling the need to monitor blood sugar levels closely.
What are the best over-the-counter remedies for diabetic dry mouth?
The best over-the-counter remedies for diabetic dry mouth include saliva substitutes like mouth sprays or gels that provide moisture without sugar, and biotin-based mouthwashes designed for dry mouth relief. Sugar-free lozenges or xylitol gum can also stimulate natural saliva production while being safe for blood sugar management.
Why is dry mouth a common symptom for people with diabetes?
Dry mouth is a common symptom for people with diabetes due to hyperglycemia reducing saliva flow and causing dehydration from excessive urine output. This imbalance affects the mouth’s natural lubrication, making it a frequent complaint that highlights the importance of consistent glucose monitoring.
Why is managing dry mouth important for overall diabetic health?
Managing dry mouth is important for overall diabetic health because it prevents complications like tooth decay, gum disease, and oral infections that can worsen with reduced saliva. Proper management supports better oral hygiene, reduces discomfort, and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels to avoid further health issues.
Which type of diabetes is more commonly associated with dry mouth?
Type 2 diabetes is more commonly associated with dry mouth, as it often involves insulin resistance leading to prolonged high blood sugar levels that impair saliva production. However, both type 1 and type 2 can cause this symptom, though it’s frequently reported in unmanaged type 2 cases.
How to relieve dry mouth from diabetes?
To relieve dry mouth from diabetes, focus on hydration by drinking water regularly, using humidifiers to add moisture to the air, and chewing sugar-free gum to encourage saliva. Combining this with tight blood sugar control through lifestyle adjustments can provide long-term relief and minimize recurrence.
Does low blood sugar cause dry mouth?
Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, is not typically a direct cause of dry mouth in diabetic patients, as this symptom is more commonly associated with high blood sugar levels leading to dehydration. However, during hypoglycemic episodes, some individuals may experience dry mouth indirectly due to anxiety, sweating, or rapid breathing that can contribute to temporary dryness.
Why do I have a dry mouth in the morning?
For diabetic patients, dry mouth in the morning often results from elevated blood sugar levels overnight, which increase urination and lead to dehydration, reducing saliva production while sleeping. Mouth breathing during sleep or side effects from diabetes medications can exacerbate this issue, making the mouth feel sticky upon waking. Staying hydrated throughout the day and controlling blood glucose with diet and exercise may alleviate morning dryness.
Does Mounjaro cause dry mouth at night?
Mounjaro, used for diabetes management, can indeed cause dry mouth as a side effect, which may be more noticeable at night due to reduced saliva flow during sleep and potential dehydration from the medication’s effects on appetite and fluid balance. This discomfort is common but manageable for diabetic patients by sipping water frequently and using sugar-free lozenges to stimulate saliva. If persistent, consulting a healthcare provider to adjust dosage or address underlying blood sugar issues is advisable.
Common reasons for a dry throat at night?
In diabetic patients, a dry throat at night can stem from high blood sugar causing dehydration through frequent urination, or from mouth breathing that dries out the throat during sleep. Other factors include low room humidity, allergies, or diabetes medications that reduce saliva. To ease this, diabetic individuals should maintain good hydration, use a humidifier, and monitor blood glucose to prevent overnight spikes.
Why are your lips stuck together when you wake up?
Lips sticking together upon waking is often due to dry mouth in diabetic patients, where reduced saliva overnight allows lips to adhere from dehydration linked to high blood sugar or medication side effects. This can be worsened by mouth breathing or low humidity in the bedroom environment. Drinking water before bed and applying a gentle lip balm can help diabetic patients avoid this sticky sensation in the morning.
Is there any link between dry mouth and diabetes fatigue?
Yes, there is a link between dry mouth and diabetes fatigue, as both can arise from uncontrolled high blood sugar levels that cause dehydration and energy depletion in diabetic patients. Dry mouth signals fluid loss, while fatigue stems from the body’s struggle to use glucose efficiently, often compounding each other. Proper blood sugar management through medication, diet, and hydration can reduce both symptoms and improve overall well-being.











Write a comment
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required