Table of content
- What is Lymphedema and Lymphatic System – In Depth
- Common Symptoms of Lymphedema
- Lymphedema Life Expectancy
- Common Stages of Lymphedema
- Common Treatment and Lifestyle Management in Lymphedema
- Role of Bio-Compression Therapy
- Recommended Bio-Compression Therapy Pumps
- Additional Considerations for Lymphedema Patients
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Lymphedema is a chronic condition caused by a blockage or damage in the lymphatic system, leading to lymphatic fluid buildup and swelling—typically in the legs or arms. The lymphatic system, a network of vessels, tissues, and organs, supports your immune system, maintains fluid balance, and filters excess fluid (lymph) back to the bloodstream. When this system is disrupted, lymphedema swelling occurs.
In this blog, we’ll cover lymphedema cancer life expectancy, symptoms, diagnosis, stages, and treatment options to help you manage this condition. Doctors diagnose lymphedema by assessing risk factors (like surgery or radiation) and conducting a physical exam. For confirmation, they may use lymphatic imaging, a non-invasive tool to evaluate your lymphatic system. Stay tuned for practical insights!
What is Lymphedema and Lymphatic System – In Depth
The lymphatic system consists of lymph vessels, lymph fluid, and various tissues and organs, including lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, and bone marrow, all working together to filter lymph (a colorless protein protein-rich watery fluid), fight infections, and maintain fluid balance.
Lymphedema is a chronic medical condition characterized by swelling in the body’s tissues, usually in the arms or legs. It occurs when the lymphatic system, responsible for draining lymph fluid, is compromised. This can result from genetic factors (primary lymphedema) or damage to lymph nodes and vessels due to surgery, radiation, or infection (secondary lymphedema).
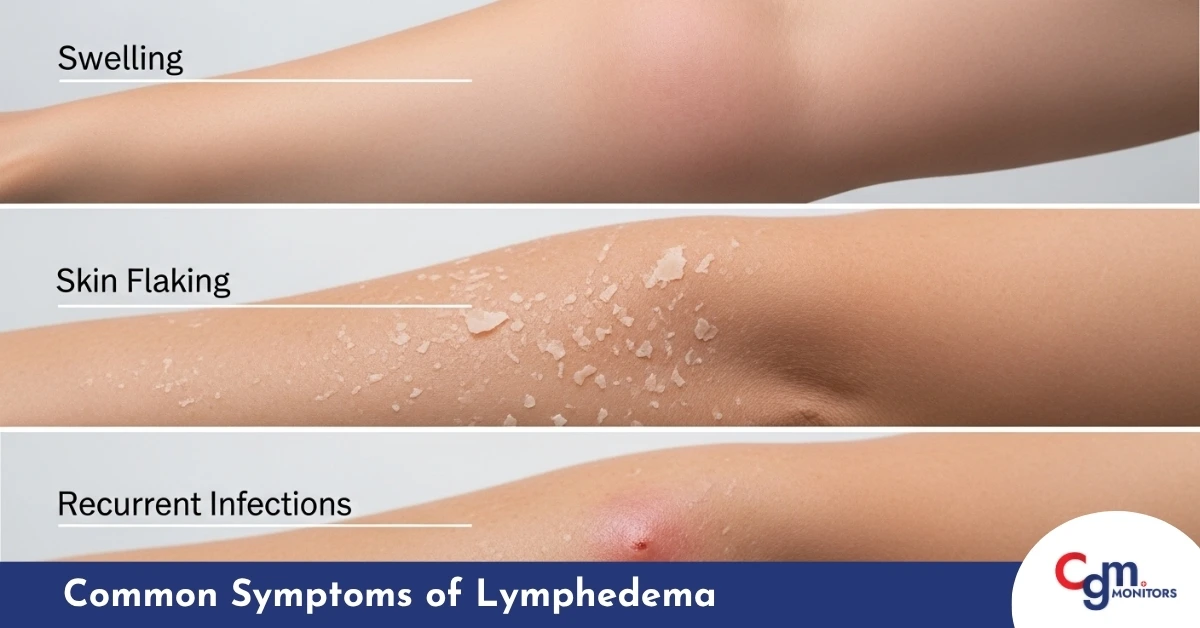
Common Symptoms of Lymphedema
Common signs include:
- Swelling: Lymph fluid typically appears in the arms or legs, but can also occur in the chest wall, abdomen, neck, genitals, or face, depending on the underlying cause.
- Skin Flaking: Dry, rough patches of skin, Scaly skin, Small, white or grey flakes of skin, Itchiness, Redness, and Cracked skin.
- Recurrent Infections: Increased susceptibility to skin infections like cellulitis.
Did you know?
1 out of 1000 people in the US experience secondary lymphedema. Move towards an easy remedy – grab your pneumatic compression system today.
Lymphedema Life Expectancy
Lymphedema itself is not life-threatening and does not directly shorten life expectancy. However, if poorly managed, it can lead to serious complications that may impact health, including:
Lymphangiosarcoma: Arising from chronic lymphedema, Lymphangiosarcoma is a rare and aggressive cancer with a survival rate of less than 5% (even with Multimodality treatment) – as per a 5-year report shared by the PubMed. Commonly observed in the upper extremities (arms) of individuals, this often arises following breast cancer surgery.
Sepsis: Lymphedema can increase the risk of infections and, in some cases, lead to sepsis. Sepsis occurs when your body’s immune system responds to an infection, becomes extremely serious, and causes damage to its own tissues and organs.
Early detection and consistent management are crucial to prevent these severe outcomes.
Common Stages of Lymphedema
Lymphedema progresses through stages, each with distinct characteristics:
-
- Stage 0 (Latent Stage): No visible swelling, but the lymphatic system is compromised.
-
- Stage I (Reversible Stage): This is mild lymphedema, pitting edema that can be reduced with elevation.
-
- Stage II (Irreversible Stage): This is moderate lymphedema. Persistent swelling with tissue fibrosis; elevation does not reduce swelling.
-
- Stage III (Elephantiasis): This is Severe Lymphedema/Elephantiasis. Severe swelling with skin changes like thickening and wart-like growths.

Common Treatment and Lifestyle Management in Lymphedema
The first step in treatment is usually a type of lymphedema therapy that helps reduce swelling. If that doesn’t work, some patients might need surgery, and suction-assisted lipectomy seems to be the most effective technique. While there’s no cure for lymphedema, various treatments can manage symptoms and prevent progression:
Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT): The first step in treatment is usually CDT. This non-invasive treatment combines manual lymphatic drainage, compression therapy, exercise, and skin care to reduce swelling, improve mobility, and prevent complications.
Compression Therapy: This therapy involves utilizing pneumatic therapy garments, e.g., lymphedema compression sleeves for legs. This applies pressure and aids lymph fluid movement.
Exercise: Engaging in gentle, low-impact activities to promote lymphatic flow.
Skin Care: Maintaining proper hygiene and moisturizing to prevent infections.
Balanced Diet: Drink plenty of water. Also, try using other herbs instead of salt, as consuming salt can help in fluid retention, which can worsen your illness.

Role of Bio-Compression Therapy
Bio-compression therapy involves using pneumatic compression devices to stimulate lymphatic drainage. These devices can be beneficial for lymphedema patients by:
- Reducing Swelling: By promoting fluid movement out of the affected area.
- Preventing Complications: Decreasing the risk of infections associated with fluid buildup.
To learn more about how a Biocompression Pump works, you can explore its mechanism in detail.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate frequency and duration of therapy, tailored to individual needs.
Recommended Bio-Compression Therapy Pumps
Selecting the right bio-compression therapy pump depends on the affected area:
- For the Arm: Devices specifically designed to fit the arm’s anatomy, providing targeted compression.
- For the Leg: Pumps designed for the lower extremities, ensuring adequate coverage from foot to thigh.
It’s advisable to consult with a lymphedema specialist to identify the most suitable model based on personal requirements.
Additional Considerations for Lymphedema Patients
Dietary Choices: Maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate additional pressure on the lymphatic system.
Avoiding Infections: Promptly addressing any skin injuries and seeking timely treatment for infections.
Sun Protection: Protecting the skin from sunburns, which can increase infection risk.
Conclusion
With appropriate care involving protection against infection, pneumatic therapies, and lifestyle adjustments, one can manage Lymphedema and live a fulfilling life. Early intervention, consistent treatment, and informed decisions are key to managing Lymphedema and preventing complications. Engaging with healthcare professionals and support networks can provide the necessary tools and resources for effective lymphedema management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the life expectancy of a person with lymphedema?
This condition does not directly affect your lifespan; however, the linked complications can pose problems. Thus, by managing lymphedema, you can live your full life.
Can you live a normal life with lymphedema?
Lymphedema has 4 stages, i.e., from stage 0 to 3. Living a normal life with proper management is possible, especially when taken care of at the early stages.
What happens to untreated lymphedema over time?
Untreated lymphedema can turn into severe skin infections, the most common of which is ‘Cellulitis’, a bacterial infection. Although rare, soft tissue cancer (lymphangiosarcoma) may also be experienced.
Can lymphedema lead to death if left untreated?
Yes, untreated lymphedema can lead to lymphangiosarcoma, an aggressive cancer with a rare long-term survival rate even with treatment.
Can proper treatment improve life expectancy in lymphedema patients?
Yes, with proper treatment of lymphedema, you can live a normal life, especially if diagnosed and treated at an earlier stage.






Write a comment
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required