Table of content
- Diabetes and How It Affects Metabolism
- Types of Diabetes and Their Metabolic Impact
- Key Metabolic Processes in Diabetes
- Hormones and Enzymes That Control Metabolism
- Complications of Diabetes and Metabolism Disorders
- Nutrition and Lifestyle in Metabolic Health
- Monitoring Metabolism with CGM Devices
- Conclusion:
- Frequently Asked Questions
Diabetes is more than just a condition of high blood sugar—it’s deeply tied to how the body processes and uses energy. At the core of this connection is metabolism, the complex system of chemical reactions that converts food into fuel. When metabolism is disrupted, it directly impacts glucose regulation, insulin response, and long-term health.
In today’s world, advanced technologies such as Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) devices—like the Dexcom G7, FreeStyle Libre 3 Plus, and Omnipod 5—are transforming how people manage their glucose and metabolism. This blog explores the relationship between diabetes and metabolism, and how CGM sensors can play a critical role in achieving better outcomes.
Diabetes and How It Affects Metabolism
Diabetes mellitus occurs when the body cannot properly regulate blood glucose levels due to problems with insulin production or insulin resistance. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a vital role in helping cells absorb glucose for energy. Without effective insulin action, the body cannot efficiently handle carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism. This leads to elevated glucose levels (hyperglycemia) and disrupts the body’s overall energy balance.
Types of Diabetes and Their Metabolic Impact
- Type 1 Diabetes – Normally detected in children and young adults, this type results from the immune system attacking insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, which leads to little or no insulin production.
- Type 2 Diabetes – The most common type, often linked to insulin resistance, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. Mostly occurs in adults, this kind happens when the body is unaffected by insulin or when the pancreas is unsuccessful in producing sufficient insulin.
- Gestational Diabetes – Happens in pregnancy and generally resolves after childbirth, but it raises the danger of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Prediabetes – A warning stage where glucose metabolism is impaired but not yet diabetes.
- MODY and LADA – Less common forms that still affect insulin and metabolism.
Each type alters how the body processes energy, making real-time glucose monitoring critical for proper management.
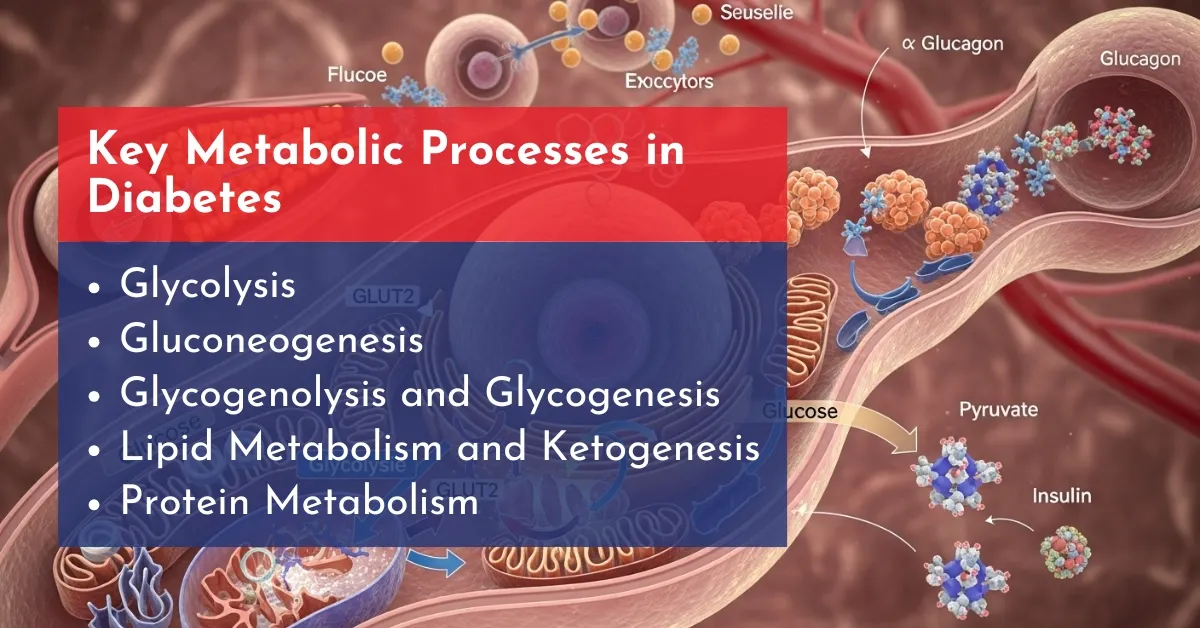
Key Metabolic Processes in Diabetes
Diabetes disrupts normal metabolism, affecting how the body handles energy from glucose, fats, and proteins. Here’s a breakdown of the main pathways involved:
- Glycolysis: This process breaks down glucose to generate energy (ATP) in cells. In diabetes, impaired insulin function hinders glucose uptake, reducing efficient energy production.
- Gluconeogenesis: The liver and kidneys produce new glucose from non-carbohydrate sources like amino acids and lactate. In diabetes, this pathway ramps up excessively, contributing to high blood sugar levels.
- Glycogenolysis and Glycogenesis: Glycogenolysis releases stored glucose from liver glycogen during fasting, while glycogenesis stores excess glucose as glycogen after meals. Diabetes often leads to unregulated release, causing blood sugar spikes.
- Lipid Metabolism and Ketogenesis: With limited glucose availability, the body shifts to breaking down fats for energy, producing ketones with the help of an enzyme called Liptin. This can escalate to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a dangerous buildup of acids in the blood.
- Protein Metabolism: Insulin deficiency promotes muscle protein breakdown (catabolism) to supply amino acids for gluconeogenesis, leading to muscle wasting and poor tissue repair.
These imbalances frequently result in symptoms like persistent fatigue, unexplained weight loss or gain, and long-term complications such as neuropathy or cardiovascular issues. Managing diabetes often focuses on restoring this metabolic harmony through diet, exercise, and medication.
Hormones and Enzymes That Control Metabolism
Besides insulin, other hormones influence metabolism:
- Glucagon – Raises blood glucose by stimulating glycogen breakdown.
- Cortisol – A stress hormone that increases glucose production.
- Leptin & Adiponectin – Regulate fat metabolism and appetite.
- GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) – Enhances insulin secretion and helps lower glucose.
An imbalance in these hormones contributes to obesity, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and cardiovascular complications.
Complications of Diabetes and Metabolism Disorders
When metabolism and glucose regulation break down, complications arise:
- Hyperglycemia and Hypoglycemia – Dangerous glucose fluctuations.
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) – A life-threatening metabolic state.
- Metabolic Syndrome – A cluster of risk factors including high blood pressure, abdominal obesity, and abnormal cholesterol.
- Long-term risks include cardiovascular disease, oxidative stress, and fatty liver disease.
Monitoring glucose closely with CGM sensors helps detect these risks early.
Nutrition and Lifestyle in Metabolic Health
Managing diabetes and metabolism requires lifestyle adjustments:
- Low-Glycemic-Index Foods – Prevent spikes in blood sugar, like adding lentils to your daily routine.
- Carbohydrate Counting – Easier with real-time CGM readings.
- High-Fiber Diets – Improve insulin sensitivity.
- Exercise and Weight Management – Boost metabolic efficiency.
- Intermittent Fasting – May help regulate insulin resistance.
- Gut Microbiome Support – Emerging link between gut health and glucose control.
CGM devices allow users to see how their diet and activity impact glucose instantly, making lifestyle changes more effective.
Monitoring Metabolism with CGM Devices
Traditional blood glucose meters only provide snapshots, but Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) shows real-time trends.
- Dexcom G6 & Dexcom G7 – Accurate, real-time tracking with mobile app integration.
- FreeStyle Libre 2 & 3 – Easy-to-use sensors with long wear time.
- Omnipod 5 G6 Intro Kit – Combines CGM and insulin delivery for automated diabetes management.
With CGMs, patients can:
- Detect hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia early.
- Track patterns in response to exercise, stress, and meals.
- Share data with healthcare providers for personalised care.
- Optimize carbohydrate intake and insulin dosing.
Conclusion:
The connection between diabetes and metabolism is undeniable—when metabolism falters, glucose control suffers. But thanks to modern tools like CGM sensors, individuals can take control of their health, monitor their glucose in real-time, and prevent complications.
Whether you are living with Type 1, Type 2, or gestational diabetes, or even at risk of metabolic syndrome, CGM devices provide the insights you need for better outcomes. Explore our collection of Dexcom, FreeStyle Libre, and Omnipod CGM systems to start your journey toward healthier living.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does metabolism affect blood sugar levels in diabetes?
Metabolism converts food into energy. When it’s disrupted in diabetes, glucose remains in the blood, causing high blood sugar. CGM devices help track these changes in real time.
Can improving metabolism help reverse Type 2 diabetes?
Yes. Better metabolism through diet, exercise, and weight control can improve insulin sensitivity and sometimes lead to remission. CGM sensors show how lifestyle changes impact glucose.
What role does the thyroid play in diabetes and metabolism?
Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism. Low thyroid activity slows metabolism and raises blood sugar, while high activity can cause unstable glucose levels. CGMs help detect these fluctuations.
How does stress impact glucose metabolism in diabetics?
Stress hormones like cortisol raise blood sugar and reduce insulin sensitivity. CGMs can reveal stress-induced glucose spikes for better management.
Are there natural ways to boost metabolism for better blood sugar control?
Yes. Eat high-fiber foods, exercise regularly, sleep well, manage stress, and track glucose with a CGM to see the effects.
How does intermittent fasting affect insulin sensitivity and metabolism?
Fasting can improve insulin sensitivity and stabilize glucose, but diabetics should monitor levels with a CGM to avoid hypoglycemia.
Can metabolic rate changes influence weight management in diabetes?
Yes. A slower metabolism makes weight loss harder and affects glucose control, while a faster metabolism improves energy use. CGMs help track these effects.
What is the connection between diabetes, metabolism, and fatigue?
Poor glucose metabolism limits energy supply to cells, causing fatigue. CGMs can identify patterns of high or low glucose linked to tiredness.





Write a comment
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required